Introduction
Electric vehicle (EV) charging has become a crucial aspect of modern transportation. The term “Granny EV Charger” often pops up in conversations about EV charging. This colloquial term refers to a basic, portable charger that plugs into a standard household outlet. Understanding the different types of EV chargers, including what is a granny EV charger, helps drivers make informed decisions about their charging needs.
What is a Granny EV Charger?
Understanding the Basics of a Granny EV Charger
Definition and Origin of the Term
A Granny EV Charger refers to a portable electric car charger that uses a domestic socket for slow charging. The term “granny charger” originates from the idea that even a grandmother can use it due to its simplicity. This charger typically includes a standard household electrical plug on one end and an EV connector on the other.
Common Uses and Applications
Granny EV Chargers serve as a convenient solution for charging electric vehicles at home. Most EV manufacturers recommend using these chargers as a supplementary method rather than the primary means of charging. Tahese chargers are ideal for situations where access to a public charging point is unavailable. They provide a reliable option for charging at home, work, or while traveling.
How Does a Granny EV Charger Work?
Technical Specifications
A Granny EV Charger connects to a standard 10 amp socket, delivering a modest 2.3kW output. This charger includes a Type 2 Charging cable, which is compatible with most electric vehicles. The design ensures easy portability, allowing users to charge their vehicles wherever a standard socket is available.
Charging Speed and Efficiency
Granny EV Chargers offer a slower charging speed compared to other options. Charging an electric vehicle with a granny charger can take several hours, depending on the battery size. Despite the slower speed, these chargers provide a practical solution for overnight charging or in emergency situations.
Types of Granny EV Chargers
Standard Household Outlet Chargers
Standard household outlet chargers represent the most basic type of Granny EV Charger. These chargers plug directly into a domestic socket and connect to the vehicle using an EV connector. They offer a straightforward and accessible way to charge an electric vehicle at home.
Portable Chargers
Portable chargers provide more flexibility compared to standard household outlet chargers. These chargers can be used in various locations, including homes, workplaces, and travel destinations. The portability of these chargers makes them a valuable tool for EV owners who need a reliable charging option on the go.
Pros and Cons of Using a Granny EV Charger
Advantages
Convenience and Accessibility
Granny EV Chargers offer unparalleled convenience. Users can plug these chargers into any standard household outlet. This feature allows for easy charging at home, work, or while traveling. The simplicity of the design ensures that even those unfamiliar with electric vehicles can use the charger without difficulty. Many EV owners appreciate the accessibility of granny chargers, especially in areas where public charging stations are scarce.
Cost-Effectiveness
Granny EV Chargers provide a cost-effective solution for electric vehicle charging. These chargers typically come included with the purchase of an electric vehicle, eliminating the need for additional investment. The use of a standard household outlet means no extra installation costs. For those who only need occasional charging, granny chargers present an economical option compared to more advanced charging systems.
Disadvantages
Slower Charging Times
One significant drawback of using a Granny EV Charger is the slower charging speed. These chargers deliver a modest 2.3kW output, which means charging an electric vehicle can take several hours. For drivers who require quick turnaround times, this slow charging rate may prove inconvenient. Dedicated home charging units or public charging stations offer significantly faster charging speeds.
Potential Safety Concerns
Safety concerns also arise with the use of Granny EV Chargers. Prolonged use of a standard household outlet for charging can lead to overheating and potential electrical hazards. Most EV manufacturers recommend using these chargers only as a backup solution. Professional installation of dedicated home charging units ensures safer and more efficient charging sessions. Regular inspection and maintenance of the charger and outlet can mitigate some safety risks.
Safety Tips for Using a Granny EV Charger
Proper Installation and Usage
Ensuring Electrical Compatibility
Granny EV Chargers must connect to a standard household outlet. Ensure that the socket can handle the charger’s power requirements. The National Electric Code (NEC) mandates that all charging stations receive NRTL certification. This certification guarantees that the charger meets safety standards. Always verify that the household wiring supports the charger’s load. Avoid using extension leads unless necessary. If used, ensure the extension lead is plugged into a socket, not another extension lead.
Avoiding Overheating
Overheating poses a significant risk when using a Granny EV Charger. Monitor the charger and the outlet during use. Avoid placing the charger near flammable materials. Ensure proper ventilation around the charging area. Regularly inspect the charger for signs of wear or damage. Damaged chargers can cause overheating and pose safety hazards. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for safe operation.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Checking for Wear and Tear
Regular maintenance ensures the longevity and safety of a Granny EV Charger. Inspect the charger and cables for any signs of wear and tear. Look for frayed wires, cracks, or other damage. Replace damaged components immediately. Using a damaged charger can harm the vehicle and pose safety risks. Ensure that the EV connector remains in good condition. A well-maintained charger operates more efficiently and safely.
Keeping the Charger Clean
Keeping the charger clean enhances its performance and safety. Dust and debris can accumulate on the charger and connectors. Use a dry cloth to wipe down the charger regularly. Avoid using water or cleaning agents that can damage the charger. Ensure that the charging port on the vehicle remains clean. A clean charger provides a more reliable connection and reduces the risk of electrical issues.
Comparing Granny EV Chargers to Other Charging Options
Level 1 vs. Level 2 Chargers
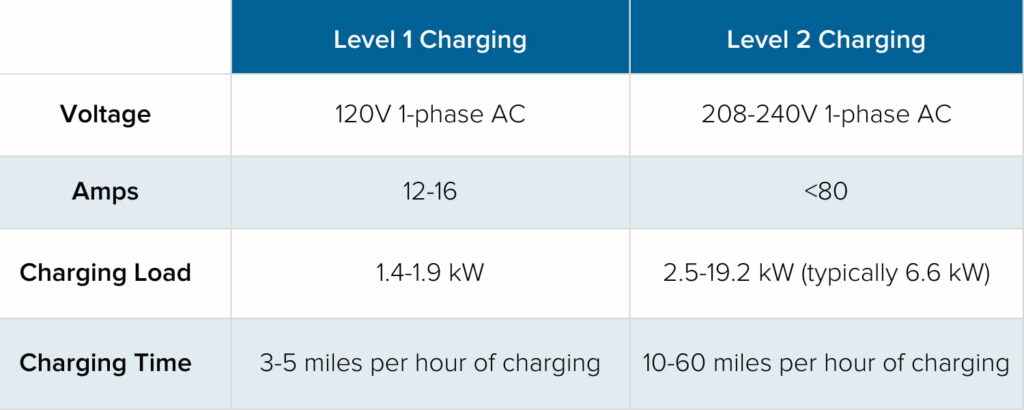
Differences in Charging Speed
Granny EV Chargers fall under the category of Level 1 chargers. These chargers use a standard household outlet and deliver a modest 2.3kW output. This results in slower charging times, often taking several hours to fully charge an electric vehicle. In contrast, Level 2 chargers provide significantly faster charging speeds. These chargers use a 240-volt outlet and can deliver between 3.7kW to 22kW. This allows for a much quicker turnaround, often charging an electric vehicle in just a few hours.
Cost and Installation Requirements
Level 1 chargers, including Granny EV Chargers, require no special installation. Users can plug these chargers into any standard household outlet, making them cost-effective and easy to use. Level 2 chargers, however, require professional installation. This involves setting up a dedicated 240-volt outlet, which can incur additional costs. Despite the higher initial investment, Level 2 chargers offer more efficient and faster charging, making them ideal for regular use.
Public Charging Stations
Availability and Convenience
Public charging stations offer another alternative to Granny EV Chargers. These stations are available in various locations, including shopping centers, parking lots, and highways. Public charging stations provide convenience for drivers who need to charge their vehicles while away from home. Many public stations offer fast-charging options, allowing for quick top-ups during short stops.
Cost Comparison
Using a Granny EV Charger at home incurs minimal costs, as it uses the household electricity supply. Public charging stations, on the other hand, often charge fees based on the amount of electricity used or the time spent charging. Some public stations offer subscription plans, which can provide cost savings for frequent users. Despite the potential costs, public charging stations offer the advantage of faster charging speeds and greater convenience.










