Introduction
In the fast-paced world of electric vehicles (EVs), where rapid advancements in technology seem to occur almost daily, the debate between slow charging and fast charging has become a central point of discussion. As the EV market expands and more people consider making the switch to electric transportation, understanding the nuances of charging speeds and their impact on EV batteries becomes crucial. In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of slow charging for an EV battery, shedding light on the key aspects of this essential topic.
EV Charging Basics
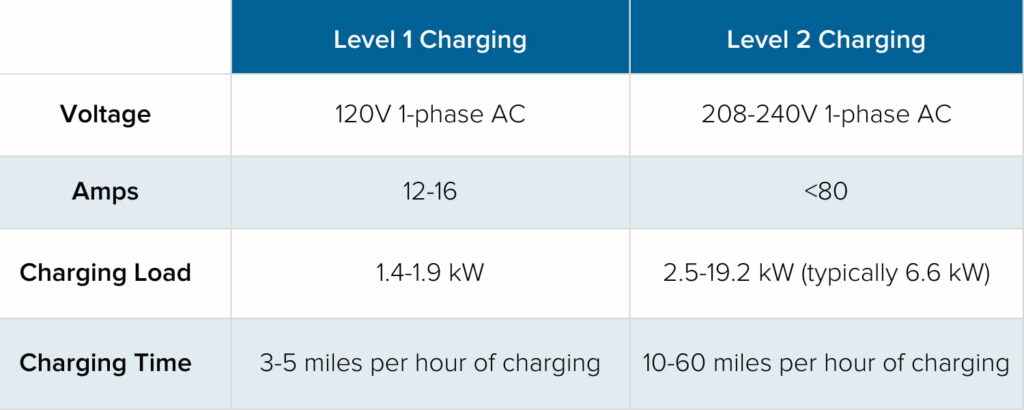
Before delving into the world of slow charging, it’s important to understand the two primary types of charging commonly available for EVs: Level 2 EV charging, portable EV chargers and EV charging wallbox.
Level 2 EV Charging: Level 2 chargers are typically found at dedicated EV charging stations, both public and private. They offer a higher charging speed compared to standard home charging, making them an attractive option for users looking to quickly top up their batteries. These chargers operate at 240 volts and can deliver around 10-60 miles of range per hour of charging, depending on the EV model.
Portable EV Chargers: Portable EV chargers, on the other hand, are designed for convenience and flexibility. They are commonly used for home charging and come with a standard 120-volt plug in North America. While they are slower compared to Level 2 chargers, portable EV chargers allow users to charge their EVs from standard household outlets, making them an excellent choice for those without easy access to a dedicated charging station.
EV Charging Wallbox: An EV charging station wallbox, often simply referred to as a “wallbox”, which is a specialized device used for electric vehicle (EV) charging. It’s designed to be mounted on a wall, typically in a garage, carport, or another convenient location near your parking space. The wallbox provides a safe and efficient way to charge your EV at home or in other private settings. Wallboxes are usually Level 2 chargers, which means they operate at higher voltages (typically 240 volts) compared to standard household outlets (120 volts). This results in faster charging times, making them ideal for overnight charging.
GREENC’s Wallboxes are designed with safety in mind. They come with features such as overcurrent protection, ground fault protection, and temperature monitoring to safeguard your EV and your home’s electrical system.
The Pros of Slow Charging
Battery Health: Slow charging is often gentler on an EV’s battery compared to fast charging. This is because slow charging generates less heat, which can be detrimental to battery longevity. When you slow charge your EV, it reduces the risk of battery degradation over time, potentially extending the lifespan of your battery pack.
Cost-Effective: Charging your EV at home with a standard portable charger is generally more cost-effective than using fast-charging stations. Slower charging consumes less electricity, resulting in lower utility bills. Furthermore, if you charge during off-peak hours, you may benefit from reduced electricity rates.
Convenient for Home Charging: Slow charging is extremely convenient for home use. You can plug in your EV when you arrive home and let it charge overnight, ensuring that it’s ready to go in the morning without needing to make an extra trip to a charging station.
Wider Availability: Slow charging is more widely available than fast charging. Virtually every home or building has standard electrical outlets, making it accessible to a broader range of EV owners. This is especially advantageous in areas with limited fast charging infrastructure.
The Cons of Slow Charging
Longer Charging Times: Slow charging takes significantly longer to replenish an EV’s battery compared to fast charging. If you’re in a hurry or need to cover a long distance, slow charging may not be the most practical option.
Limited Range: Slow charging is suitable for daily commuting and regular errands but may not provide enough range for longer trips without extended charging stops. This limitation can be frustrating for those who frequently travel long distances.
Dependency on Home Charging: Slow charging is heavily dependent on home charging infrastructure. If you don’t have a dedicated parking spot with access to an electrical outlet, slow charging may not be a viable option for you.
Charging Network Gaps: In some regions, the availability of Level 2 charging stations is limited, leading to potential inconvenience for EV owners relying on slow charging. This can be especially problematic when traveling to areas with inadequate charging infrastructure.
Finding the Right Balance: Fast vs. Slow Charging
Ultimately, the choice between slow charging and fast charging depends on your specific needs and circumstances. There are some considerations to help you find the right balance:
Daily Commute: If you primarily use your EV for daily commuting and have access to home charging, slow charging is a practical and cost-effective choice.
Longer Trips: For longer trips, especially if you’re in a hurry, fast charging at Level 3 charging stations (DC fast chargers) is essential to minimize charging stops and downtime.
Battery Health: If you plan to keep your EV for an extended period and want to maximize battery health, consider mixing slow charging at home with occasional fast charging when necessary.
Charging Network: Evaluate the availability of Level 2 charging stations and Level 3 fast charging stations in your area and along your typical routes. This will help you plan your charging strategy effectively.
Conclusion
Slow charging for an EV battery comes with both pros and cons. It offers several advantages, including better battery health and cost-effectiveness, especially for daily use and home charging. However, it may not be suitable for all situations, such as long-distance travel or when fast charging infrastructure is readily available. To get the best of both worlds, many EV owners opt for a hybrid approach, utilizing slow charging for routine use and fast charging when needed to strike a balance between battery preservation and convenience. As the EV charging network continues to evolve, the choice between slow and fast charging will become more nuanced, allowing EV owners to tailor their charging habits to their individual needs.







