Introduction
The GB/T Charging Standards define the framework for electric vehicle charging in China. These standards play a crucial role in the advancement of electric vehicles. The GB/T standards ensure compatibility and safety in the charging process. The global electric vehicle market recognizes the importance of these standards. Many manufacturers adopt the GB/T standards to access the Chinese market. Understanding what is GBT standard for EV charging provides insights into its impact on international trade and technology development.
What is GB/T Standard for EV Charging
Definition and Scope
What GB/T Covers
The GB/T standard for EV charging defines the guidelines for electric vehicle charging in China. This standard addresses both AC and DC charging methods. The GB/T standard ensures safe and efficient charging processes. It establishes protocols for communication between chargers and electric vehicles. Manufacturers must adhere to these standards to sell vehicles in China. The GB/T standard also includes safety measures like insulation monitoring and temperature control.
Key Technical Specifications
The GB/T standard specifies technical requirements for charging interfaces. These specifications include high-power charging capabilities. The latest version supports up to 1.2 megawatts of power. The GB/T standard incorporates a DC control pilot circuit. This feature enhances safety during the charging process. The standard also outlines electronic locking mechanisms. These mechanisms prevent unauthorized disconnection during charging.
Historical Development
Origins and Evolution
The GB/T standard originated in China. The Chinese government introduced it to regulate EV charging. The standard has evolved over time. Initial versions focused on basic charging needs. Later updates addressed advanced technologies. The evolution reflects China’s commitment to electric mobility. The GB/T standard now plays a vital role in the global EV market.
Milestones in Adoption
Several milestones mark the adoption of the GB/T standard. China implemented the standard as a national requirement. This move encouraged widespread use among manufacturers. The GB/T standard gained recognition internationally. Many countries now consider it a benchmark for EV charging. The ChaoJi-1 standard builds upon the GB/T protocol. This new standard aims for global compatibility by 2024.
Technical Aspects of GB/T
Charging Protocols
AC vs. DC Charging
The GB/T standard for EV charging defines protocols for both AC and DC charging methods. AC charging involves alternating current, which is commonly used for residential and public charging stations. The process of AC charging typically takes longer due to lower power levels. DC charging, on the other hand, uses direct current and provides faster charging times. High-power DC charging stations can deliver up to 1.2 megawatts, as specified by the GB/T standard. This capability makes DC charging suitable for commercial and highway locations. Understanding what is GBT standard for EV charging helps in recognizing the importance of these protocols.
Communication Standards
Communication between the electric vehicle and the charger is crucial. The GB/T standard outlines specific communication protocols to ensure safety and efficiency. These protocols facilitate the exchange of information between the vehicle’s battery management system and the charger. The communication standards help monitor charging status, control power flow, and ensure proper connection. The GB/T standard also includes features like insulation monitoring and electronic locking mechanisms. These features prevent unsafe charging modes and unauthorized disconnection. The understanding of what is GBT standard for EV charging highlights the significance of these communication protocols.
Compatibility and Interoperability
Vehicle and Charger Compatibility
The GB/T standard ensures compatibility between electric vehicles and charging stations. Manufacturers must design vehicles and chargers that adhere to these standards to operate in China. The standard specifies the physical and electrical requirements for connectors and interfaces. This ensures that any compliant vehicle can charge at any GB/T-compatible station. Compatibility plays a vital role in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. The knowledge of what is GBT standard for EV charging is essential for manufacturers aiming to enter the Chinese market.
Interoperability with Other Standards
Interoperability refers to the ability of different systems to work together. The GB/T standard aims to achieve interoperability with other global charging standards. The ChaoJi-1 standard, based on GB/T, seeks compatibility with all DC fast charging stations worldwide. This initiative promotes international collaboration and facilitates global trade. Interoperability reduces barriers for manufacturers and consumers alike. Understanding what is GBT standard for EV charging provides insights into its impact on international interoperability efforts.
Comparison with Other Global Standards
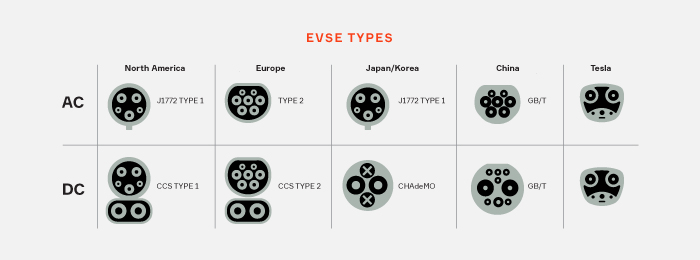
GB/T vs. CCS
Technical Differences
The GB/T standard and the CCS standard serve electric vehicle charging but have distinct technical features. GB/T focuses on both AC and DC charging, with high-power capabilities reaching up to 1.2 megawatts. CCS, or Combined Charging System, integrates AC and DC charging in a single connector. CCS supports fast charging but typically offers lower power levels compared to GB/T. The GB/T standard includes advanced safety measures like insulation monitoring. CCS emphasizes a universal connector design for ease of use.
Market Adoption
China predominantly uses the GB/T standard due to government regulations. This widespread adoption makes GB/T essential for manufacturers targeting the Chinese market. CCS finds popularity in Europe and North America. Many automakers in these regions prefer CCS for its compatibility with existing infrastructure. The global market sees both standards as vital, with each serving different geographical needs. Understanding what is GBT standard for EV charging helps in recognizing its influence on market dynamics.
GB/T vs. CHAdeMO
Technical Differences
GB/T and CHAdeMO both support DC fast charging but differ in design and technology. GB/T offers higher power levels, supporting up to 1.2 megawatts. CHAdeMO typically provides lower power outputs, focusing on reliability and safety. The GB/T standard incorporates a DC control pilot circuit for enhanced safety. CHAdeMO uses a separate communication protocol to manage charging. Both standards prioritize safety but employ different methods to achieve it.
Market Adoption
The GB/T standard dominates the Chinese market, driven by national policies. CHAdeMO finds usage in Japan and some parts of Europe. Automakers in Japan often integrate CHAdeMO due to local preferences. The global market sees a mix of both standards, with regional variations influencing adoption. Understanding what is GBT standard for EV charging highlights its role in shaping international market trends.
Impact on the Global EV Market
Influence on International Trade
Export and Import Considerations
The GB/T charging standard significantly affects international trade. Manufacturers must comply with the GB/T standard to export electric vehicles to China. The Chinese market demands adherence to specific technical requirements. Non-compliance can lead to restricted market access. Understanding what is GBT standard for EV charging becomes crucial for global manufacturers. The GB/T standard influences import regulations in many countries. Countries importing Chinese electric vehicles need compatible infrastructure. This requirement may necessitate adjustments in existing charging networks.
Partnerships and Collaborations
The GB/T standard fosters partnerships and collaborations. International companies often collaborate with Chinese firms to meet GB/T requirements. These partnerships facilitate technology exchange and innovation. Joint ventures focus on developing compatible charging solutions. Understanding what is GBT standard for EV charging aids in forming strategic alliances. Collaborations enhance the global reach of electric vehicle technologies. Companies benefit from shared expertise and resources. The GB/T standard plays a pivotal role in these cooperative efforts.
Challenges and Opportunities
Adoption Barriers
Adoption barriers exist for the GB/T standard outside China. Infrastructure compatibility poses a significant challenge. Existing charging networks may require upgrades to support GB/T. The cost of infrastructure changes can deter adoption. Understanding what is GBT standard for EV charging helps identify these challenges. Regulatory differences between countries create additional hurdles. Harmonizing standards across regions remains a complex task. Overcoming these barriers requires coordinated efforts from stakeholders.
Future Prospects
The future prospects of the GB/T standard appear promising. Technological advancements continue to enhance its capabilities. Emerging technologies offer opportunities for improved efficiency. Understanding what is GBT standard for EV charging provides insights into these developments. The GB/T standard may see increased adoption globally. Countries recognize the benefits of a unified charging protocol. Strategic implications include expanded market access for manufacturers. The GB/T standard’s evolution will shape the future of electric mobility.
Future of GB/T Charging Standards
Technological Innovations
Emerging Technologies
The GB/T charging standards continue to evolve with emerging technologies. New advancements in battery technology promise faster charging times. Researchers focus on increasing energy density in batteries. Improved energy density allows for longer driving ranges. Wireless charging technology also gains attention. Wireless systems offer convenience by eliminating cables. These innovations enhance the appeal of electric vehicles.
Potential Upgrades
Potential upgrades to the GB/T standards aim to improve efficiency. Engineers work on optimizing the communication protocols. Enhanced protocols ensure seamless interaction between vehicles and chargers. Safety features receive continuous updates. New safety measures address potential risks during charging. The GB/T standards may incorporate advanced cooling systems. Effective cooling prevents overheating during high-power charging sessions. These upgrades contribute to a safer and more efficient charging experience.
Global Expansion
Adoption in Other Countries
The GB/T charging standards seek adoption beyond China. Some countries express interest in integrating these standards. Adoption requires infrastructure adjustments to accommodate GB/T chargers. Policymakers evaluate the benefits of standardization. Standardization simplifies the charging process for international travelers. Countries with strong trade ties to China consider adopting GB/T standards. Adoption facilitates smoother electric vehicle imports and exports.
Strategic Implications
Strategic implications arise from the global expansion of GB/T standards. Manufacturers gain access to broader markets by complying with GB/T requirements. Compliance ensures compatibility with a wide range of charging stations. International collaboration strengthens as countries adopt common standards. Shared standards promote technological exchange and innovation. The GB/T standards influence global electric vehicle policies. Policymakers recognize the importance of harmonized charging protocols.








